Padova-Asiago Supernova Group
Highlights
The correlation of rate of Type Ia Supernovae with the parent galaxy properties: lights and shadows
Greggio, L. and Cappellaro, E. 2019 Astron Astroph 625, 113 (link to pdf)
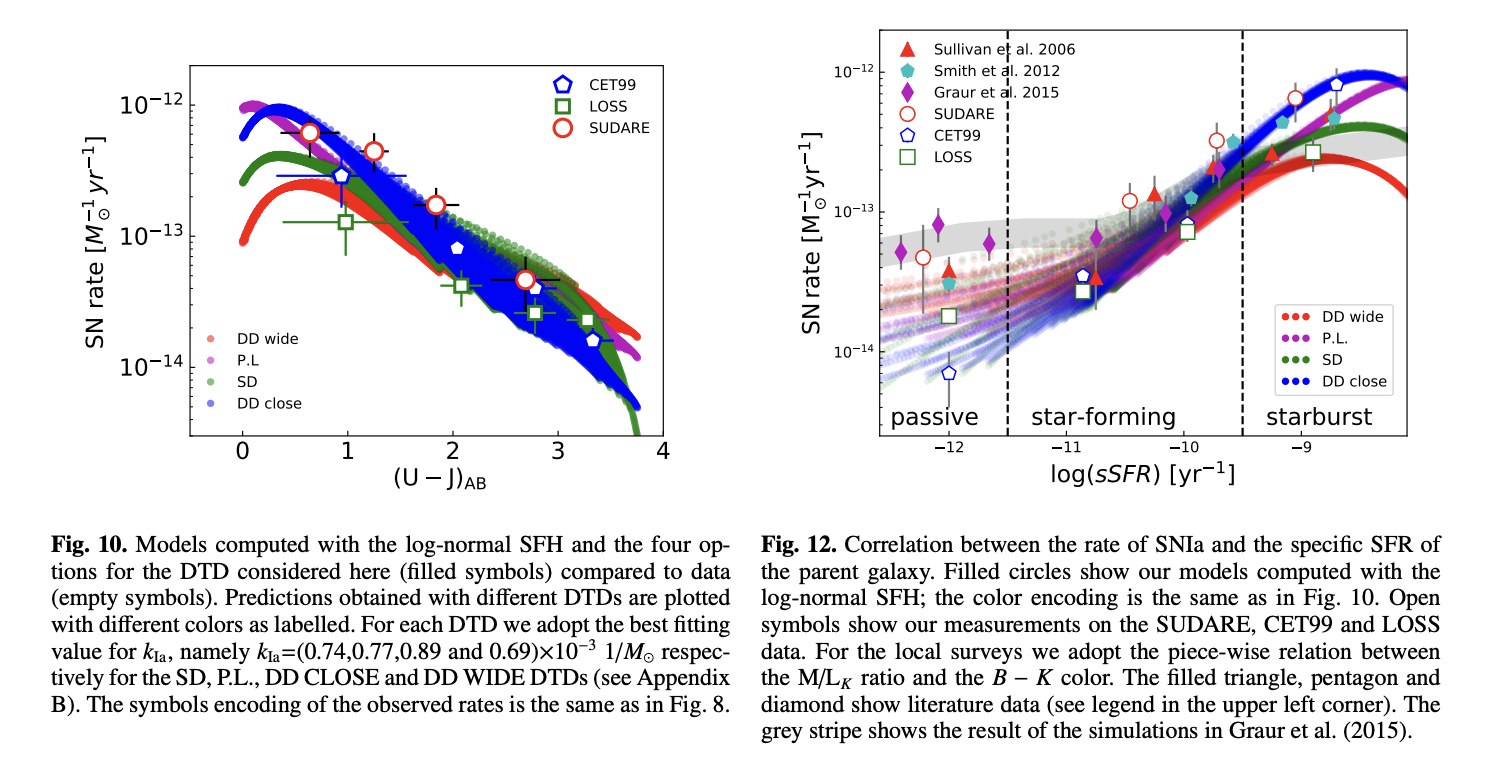
The identification of the progenitors of Type Ia Supernovae (SNIa) is extremely important in several astrophysical contexts, ranging from stellar evolution in close binary systems to evaluating cosmological parameters. Determining the distribution of the delay times (DTD) of SNIa progenitors can shed light on their nature. In this paper we investigate on the diagnostic capabilities on the DTD of the correlation between the SNIa rate and the parent galaxy properties by examining its systematics with the various parameters at play: simple stellar population models, the adopted description for the star formation history in galaxies, and the way in which the masses of the galaxies are evaluated. We compute models for the correlations of the SNIa rate with the parent galaxy color and specific star formation rate for a variety of input ingredients, and for a few astrophysically motivated DTD laws. The models are compared to the results of three independent observational surveys. We find that the scaling of the SNIa rate with the properties of the parent galaxy is sensitive to all input ingredients mentioned above. This is a severe limitation on the possibility to discriminate alternative DTDs. In addition, current surveys show some discrepancies for the rate measured in the reddest and bluest galaxies, likely due to limited statistics and inhomogeneity of the observations. For galaxies with intermediate colors the rates are in agreement, leading to a robust determination of the productivity of SNIa from stellar populations of ≃ 0.8 events per 1000 \msun. Large stastistics of SNIa events along with accurate measurements of the star formation history in the galaxies are required to derive firm constraints on the DTD. LSST will achieve these results by providing the homogeneous, unbiased and vast database on both SNIa and galaxies. 189